🔍 Introduction
The Superposition Principle is a powerful tool in circuit analysis, allowing engineers to break down complex circuits into simpler components. It is particularly useful for linear circuits with multiple independent sources, helping to determine voltage and current contributions from each source separately.
💡 What Is the Superposition Principle?
The Superposition Principle states that in any linear circuit with multiple independent sources, the total response (voltage or current) at any point is the sum of the individual responses caused by each source acting alone.
🎯 Key Steps in Applying the Superposition Principle
1️⃣ Turn off all independent sources except one – Replace voltage sources with short circuits and current sources with open circuits.
2️⃣ Analyze the circuit with the remaining source – Use standard circuit analysis techniques (Ohm’s Law, Kirchhoff’s Laws).
3️⃣ Repeat for each independent source – Solve the circuit separately for each source.
4️⃣ Sum the individual contributions – Add up the voltage and current values from each analysis to get the total response.
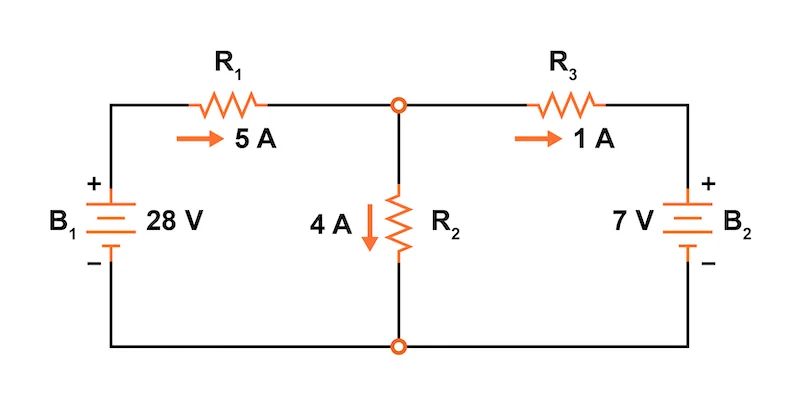
🔧 Example Application
Consider a circuit with two voltage sources and multiple resistors. Using the Superposition Principle:
✅ Step 1: Replace one voltage source with a short circuit and solve for currents.
✅ Step 2: Replace the other voltage source and solve again.
✅ Step 3: Add the individual results to obtain the final circuit behavior.
🏆 Benefits of the Superposition Principle
✅ Simplifies complex circuits – Breaks down multi-source circuits into manageable parts.
✅ Enhances accuracy – Provides precise voltage and current calculations.
✅ Applicable to AC and DC circuits – Works for both alternating and direct current systems.
🏁 Conclusion
The Superposition Principle is a fundamental concept in electrical engineering, making circuit analysis more intuitive and efficient. By isolating individual sources and summing their effects, engineers can accurately predict circuit behavior without complex simultaneous equations.
