Introduction
A home energy audit is a thorough assessment of a household’s energy consumption and efficiency, aimed at identifying areas where energy is being wasted and providing recommendations for improvement. By conducting an audit, homeowners can reduce their electricity bills, minimize their carbon footprint, and create a more sustainable living environment.
Energy audits have gained increasing importance as global energy demand rises and environmental concerns become more pressing. Governments and organizations worldwide encourage homeowners to adopt energy-efficient practices, and a home energy audit is the first step in achieving this goal. This article explores the concept of home energy audits, their benefits, the audit process, common findings, improvement recommendations, and future trends in residential energy efficiency.
Understanding Home Energy Audits
A home energy audit is an evaluation of a home’s energy use, designed to pinpoint inefficiencies and propose solutions. It typically involves analyzing electricity consumption, inspecting insulation and ventilation, and evaluating the effectiveness of appliances. Homeowners can conduct a DIY audit or hire professional auditors equipped with specialized tools to provide a detailed report.
There are two primary types of home energy audits:
- Preliminary or DIY Audit – A basic evaluation where homeowners review energy bills, inspect their home for air leaks, and assess appliance efficiency.
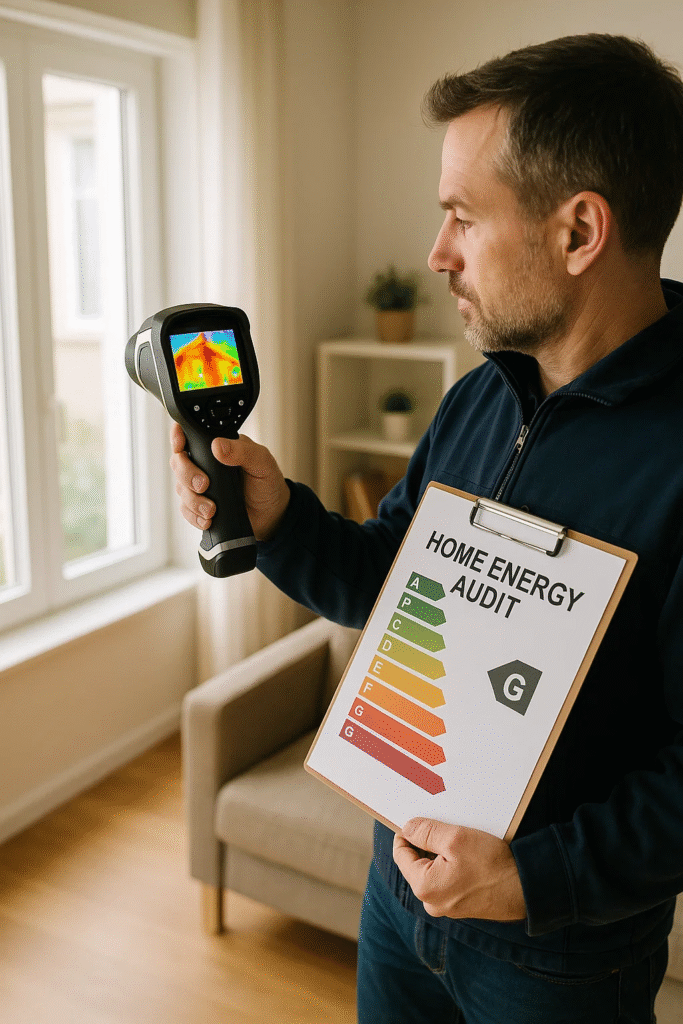
- Professional Audit – Conducted by certified auditors using advanced tools like thermal imaging cameras, blower doors, and energy meters.
Benefits of Conducting a Home Energy Audit
A home energy audit offers numerous advantages, including:
- Reduced Energy Costs: Identifying inefficiencies helps homeowners lower energy consumption and save on utility bills.
- Improved Comfort: Proper insulation and sealing eliminate drafts and maintain stable indoor temperatures.
- Environmental Impact Reduction: Decreasing energy usage results in lower carbon emissions.
- Extended Appliance Lifespan: Efficient use of appliances prevents unnecessary wear and tear.
- Increased Property Value: Energy-efficient homes are more attractive to buyers.
- Better Indoor Air Quality: Addressing ventilation issues improves overall air circulation and health conditions.
The Home Energy Audit Process
A professional energy audit follows a structured process to assess a home’s efficiency. It typically includes:
1. Reviewing Energy Bills
- Auditors examine utility bills to identify patterns and abnormal consumption levels.
- High energy costs may signal inefficient appliances or poor insulation.
2. Inspecting Insulation and Air Sealing
- Thermal imaging helps detect areas where heat escapes.
- Sealing gaps around doors, windows, and vents can significantly improve efficiency.
3. Checking HVAC Systems
- Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems are inspected for performance and efficiency.
- Old systems may consume excessive power and require upgrades.
4. Evaluating Lighting and Appliances
- Energy-efficient LED bulbs replace incandescent lights to reduce electricity consumption.
- High-energy-consuming appliances are identified for potential replacement with energy-efficient models.
5. Conducting a Blower Door Test
- A blower door test determines air leakage by depressurizing the home and measuring airflow.
- Excessive leakage means insulation and sealing improvements are necessary.
6. Assessing Water Heating Efficiency
- Water heaters are inspected for proper operation.
- Switching to tankless water heaters or setting temperature controls optimally reduces energy waste.
7. Evaluating Renewable Energy Potential
- Auditors check if the home can benefit from solar panels or other renewable energy sources.
- Assessing roof space, sun exposure, and grid integration feasibility.
Common Energy Audit Findings
Energy audits often reveal specific areas where efficiency improvements are needed. Some common findings include:
- Poor Insulation: Heat loss through poorly insulated walls, roofs, and floors.
- Air Leaks: Gaps around windows, doors, and chimneys leading to increased heating/cooling costs.
- Inefficient Appliances: Older refrigerators, washing machines, and HVAC systems consuming excessive energy.
- Lighting Inefficiencies: Homes still using incandescent bulbs instead of LEDs.
- HVAC System Issues: Ductwork leaks, dirty filters, or outdated heating and cooling units.
- Excessive Standby Power Consumption: Devices left plugged in consuming power even when switched off.
Energy Efficiency Improvement Recommendations
Based on audit findings, homeowners can take various steps to enhance efficiency:
1. Improving Insulation
- Installing fiberglass, cellulose, or spray foam insulation reduces heat loss.
- Weather stripping around windows and doors prevents air leaks.
2. Upgrading HVAC Systems
- Investing in energy-efficient air conditioners and heaters lowers energy consumption.
- Regular maintenance ensures optimal system performance.
3. Switching to LED Lighting
- LED bulbs consume 75% less energy and last significantly longer.
- Motion sensors and timers further reduce unnecessary electricity use.
4. Optimizing Appliance Use
- Using ENERGY STAR-rated appliances improves efficiency.
- Washing clothes with cold water and air-drying reduces electricity consumption.
5. Installing Smart Thermostats
- Automated temperature controls adjust settings based on occupancy and weather.
- Programmable thermostats can reduce heating and cooling costs.
6. Utilizing Renewable Energy
- Solar panel installation provides clean and cost-effective energy.
- Wind turbines or geothermal systems may be viable options depending on location.
7. Reducing Standby Power Waste
- Using smart power strips prevents unnecessary energy draw.
- Unplugging unused devices minimizes phantom loads.
Future Trends in Home Energy Auditing
As technology advances, home energy audits continue to evolve. Emerging trends include:
- AI-Powered Energy Analysis:
- AI tools analyze energy consumption patterns and provide optimization recommendations.
- Predictive analytics assist homeowners in making data-driven energy-saving decisions.
- IoT-Based Smart Homes:
- Smart home devices integrate with energy audits for automated monitoring.
- Systems detect inefficiencies and adjust settings in real time.
- Increased Adoption of Renewable Energy:
- Solar and wind power installations become more common as costs decline.
- Home battery storage solutions improve energy independence.
- Government Incentives and Green Building Certifications:
- Governments offer rebates and tax credits for energy-efficient upgrades.
- LEED and other certifications promote environmentally responsible housing.
- Blockchain for Energy Transactions:
- Blockchain enables decentralized energy trading in microgrids.
- Homeowners can sell excess solar power directly to neighbors.
Conclusion
A home energy audit is a crucial step in enhancing energy efficiency, reducing utility costs, and promoting environmental sustainability. By analyzing consumption patterns, identifying inefficiencies, and implementing recommended upgrades, homeowners can create a comfortable, cost-effective, and eco-friendly living space.
As smart technologies and renewable energy options continue to expand, home energy audits will play an even greater role in optimizing residential energy use. Whether conducted independently or by professionals, an audit is an invaluable tool for making informed energy-saving decisions.
