Introduction
The evolution of power distribution systems has led to the development of smart grids, which integrate advanced communication, automation, and control technologies to enhance efficiency, reliability, and sustainability. Traditional power grids face challenges such as energy losses, demand fluctuations, and limited integration of renewable energy sources. Smart grids address these issues by enabling real-time monitoring, decentralized energy management, and improved consumer participation. As the world moves toward a more sustainable energy future, smart grid technology plays a crucial role in transforming power distribution.
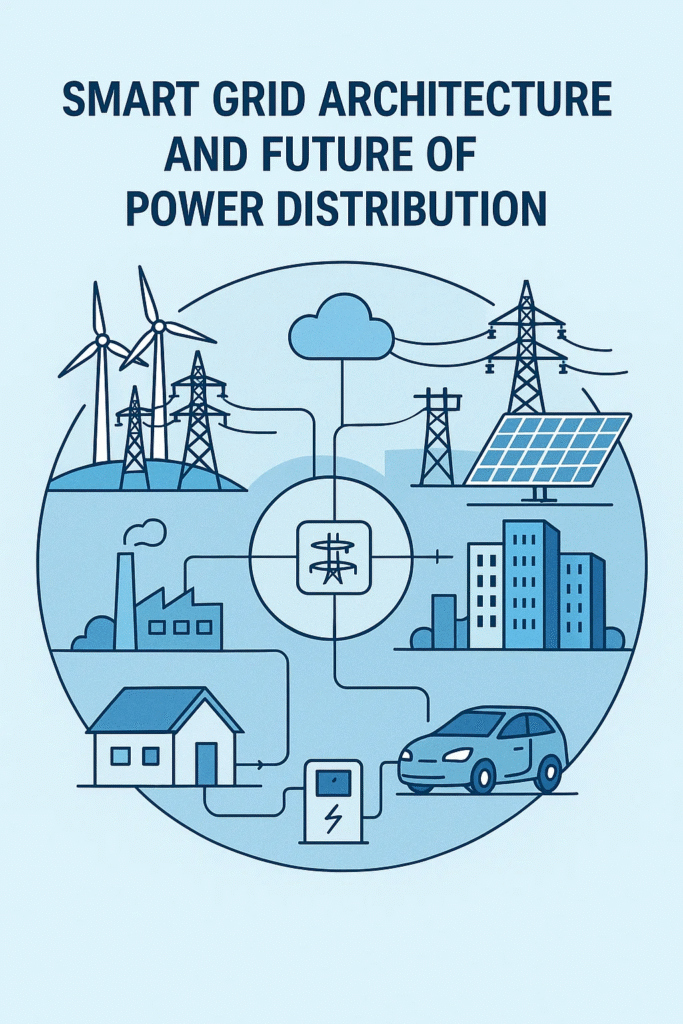
Smart Grid Architecture
A smart grid consists of multiple interconnected components that work together to optimize electricity generation, transmission, and consumption. The key elements of smart grid architecture include:
- Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI)
- Smart meters provide real-time data on energy consumption and enable two-way communication between consumers and utilities.
- They facilitate demand response programs and dynamic pricing.
- Distributed Energy Resources (DERs)
- Integration of renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power enhances grid sustainability.
- Energy storage systems, including batteries, help balance supply and demand.
- Phasor Measurement Units (PMUs)
- PMUs provide high-speed monitoring of grid stability and voltage fluctuations.
- They improve fault detection and enhance grid resilience.
- Integrated Communication Networks
- Secure and reliable communication infrastructure enables data exchange between grid components.
- Wireless and fiber-optic networks support real-time monitoring and control.
- Grid Automation and Control Systems
- Automated substations and self-healing networks enhance grid reliability.
- Artificial intelligence and machine learning optimize energy distribution.
- Cybersecurity Measures
- Protection against cyber threats ensures the integrity of smart grid operations.
- Encryption and authentication protocols safeguard data transmission.
Future of Power Distribution with Smart Grids
The future of power distribution is shaped by advancements in smart grid technology, leading to several transformative trends:
- Decentralized Energy Generation
- Microgrids and peer-to-peer energy trading empower consumers to generate and share electricity.
- Blockchain technology enhances transparency in energy transactions.
- Enhanced Grid Resilience
- Predictive analytics and AI-driven fault detection minimize outages.
- Self-healing networks restore power automatically after disruptions.
- Electrification of Transportation
- Smart grids support the integration of electric vehicles (EVs) and vehicle-to-grid (V2G) systems.
- Dynamic charging infrastructure optimizes energy distribution.
- Sustainable Energy Management
- Demand-side management programs encourage energy efficiency.
- Smart grids facilitate carbon footprint reduction and environmental sustainability.
Conclusion
Smart grid technology is revolutionizing power distribution by enhancing efficiency, reliability, and sustainability. As the global energy landscape evolves, smart grids will play a pivotal role in integrating renewable energy, improving grid resilience, and enabling consumer participation. The future of power distribution lies in intelligent, interconnected systems that optimize energy management and contribute to a sustainable energy future.
