🔍 Introduction
In electrical engineering, grounding is a fundamental concept that ensures safety, stability, and proper circuit operation. The term “ground” refers to a reference point in an electrical system from which voltages are measured, a common return path for electric current, or a direct physical connection to the Earth. Grounding plays a crucial role in preventing electrical hazards, reducing noise, and protecting equipment.
💡 What Is Electrical Grounding?
Electrical grounding provides a safe path for excess electrical energy to dissipate, preventing shocks and equipment damage. It serves as a zero-voltage reference point in circuits, ensuring proper functionality and stability.
🎯 Types of Electrical Grounding
Electrical grounding can be classified into different types based on its application:
🌍 Earth Ground
✅ Definition: A direct physical connection to the Earth using a conductive rod or plate.
✅ Purpose: Provides a path for excess electricity to safely dissipate into the ground.
✅ Application: Used in power distribution systems, lightning protection, and electrical safety.
🏗️ Chassis Ground
✅ Definition: Grounding the metal casing or frame of an electrical device.
✅ Purpose: Prevents electric shock by ensuring exposed conductive parts remain at a safe potential.
✅ Application: Found in electronic devices, appliances, and industrial equipment.
🔄 Signal Ground
✅ Definition: A reference point in electronic circuits to maintain consistent voltage levels.
✅ Purpose: Reduces electrical noise and interference in sensitive circuits.
✅ Application: Used in audio systems, communication devices, and precision instruments.
⚡ Importance of Grounding in Electrical Systems
✅ Safety: Prevents electric shocks by providing a controlled path for stray currents.
✅ Equipment Protection: Shields devices from voltage surges and lightning strikes.
✅ Noise Reduction: Minimizes interference in electronic circuits, improving signal clarity.
✅ Stable Voltage Reference: Ensures consistent voltage levels for accurate circuit operation.
🔧 How Grounding Is Implemented
Grounding is achieved using various methods:
✅ Ground Rods & Plates: Metal conductors buried in the ground for effective dissipation.
✅ Grounding Conductors: Copper or aluminum wires connecting electrical systems to ground.
✅ Bonding: Connecting all metallic parts to maintain uniform electrical potential.
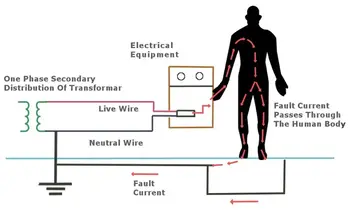
🏁 Conclusion
Grounding is essential for electrical safety, equipment protection, and circuit stability. Whether in power grids, electronic devices, or industrial systems, proper grounding ensures efficient and secure electrical operation.
Want to explore more? You can check out this resource for a deeper dive! 🚀 Let me know if you need further clarification! ⚙️🔍
